May 22 2014
Vast amounts of excess heat are generated by industrial processes and by electric power plants; researchers around the world have spent decades seeking ways to harness some of this wasted energy. Most such efforts have focused on thermoelectric devices, solid-state materials that can produce electricity from a temperature gradient, but the efficiency of such devices is limited by the availability of materials.
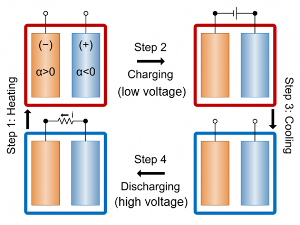 This diagram shows the stages of operation of a battery designed for heat harvesting. 1) Battery is heated so that its voltage becomes lower. 2) Battery is charged at high temperature, using low voltage. 3) Battery is cooled down, causing its voltage to become higher. 4) The battery is discharged at low temperature, with the high voltage. The voltage difference in the output comes from heat that was absorbed in the process.
This diagram shows the stages of operation of a battery designed for heat harvesting. 1) Battery is heated so that its voltage becomes lower. 2) Battery is charged at high temperature, using low voltage. 3) Battery is cooled down, causing its voltage to become higher. 4) The battery is discharged at low temperature, with the high voltage. The voltage difference in the output comes from heat that was absorbed in the process.
Now researchers at MIT and Stanford University have found a new alternative for low-temperature waste-heat conversion into electricity — that is, in cases where temperature differences are less than 100 degrees Celsius.
The new approach, based on a phenomenon called the thermogalvanic effect, is described in a paper published in the journal Nature Communications by postdoc Yuan Yang and professor Gang Chen at MIT, postdoc Seok Woo Lee and professor Yi Cui at Stanford, and three others.
Since the voltage of rechargeable batteries depends on temperature, the new system combines the charging-discharging cycles of these batteries with heating and cooling, so that the discharge voltage is higher than charge voltage. The system can efficiently harness even relatively small temperature differences, such as a 50 C difference
To begin, the uncharged battery is heated by the waste heat. Then, while at the higher temperature, the battery is charged; once fully charged, it is allowed to cool. Because the charging voltage is lower at high temperatures than at low temperatures, once it has cooled the battery can actually deliver more electricity than what was used to charge it. That extra energy, of course, doesn’t just appear from nowhere: It comes from the heat that was added to the system.
The system aims at harvesting heat of less than 100 C, which accounts for a large proportion of potentially harvestable waste heat. In a demonstration with waste heat of 60 C the new system has an estimated efficiency of 5.7 percent.
The basic concept for this approach was initially proposed in the 1950s, Chen says, but “a key advance is using material that was not around at that time” for the battery electrodes, as well as advances in engineering the system.
That earlier work was based on temperatures of 500 C or more, Yang adds; most current heat-recovery systems work best with higher temperature differences.
While the new system has a significant advantage in energy-conversion efficiency, for now it has a much lower power density — the amount of power that can be delivered for a given weight — than thermoelectrics. It also will require further research to assure reliability over a long period of use, and to improve the speed of battery charging and discharging, Chen says. “It will require a lot of work to take the next step,” he cautions.
Chen, the Carl Richard Soderberg Professor of Power Engineering and head of MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, says there’s currently no good technology that can make effective use of the relatively low-temperature differences this system can harness. “This has an efficiency we think is quite attractive,” he says. “There is so much of this low-temperature waste heat, if a technology can be created and deployed to use it.”
Cui says, “Virtually all power plants and manufacturing processes, like steelmaking and refining, release tremendous amounts of low-grade heat to ambient temperatures. Our new battery technology is designed to take advantage of this temperature gradient at the industrial scale.”
Lee adds, “This technology has the additional advantage of using low-cost, abundant materials and manufacturing process that are already widely used in the battery industry.”
Peidong Yang, a professor of chemistry at the University of California at Berkeley who was not involved in this work, says, “By exploring the thermogalvanic effect, [the MIT and Stanford researchers] were able to convert low-grade heat to electricity with decent efficiency. It is a very promising technology. … This is a clever idea, and low-grade waste heat is everywhere.”
MIT’s Yang underscores that point: “One-third of all energy consumption in the United States ends up as low-grade heat.”
The MIT work was partially funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, in part through the Solid-State Solar-Thermal Energy Conversion Center, and the U.S. Air Force. The work at Stanford was partially funded by the DOE, the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, and National Research Foundation of Korea.