Jul 10 2020
New research reveals how winners & losers from climate change can be identified based on their ability to adapt to rising future temperatures.
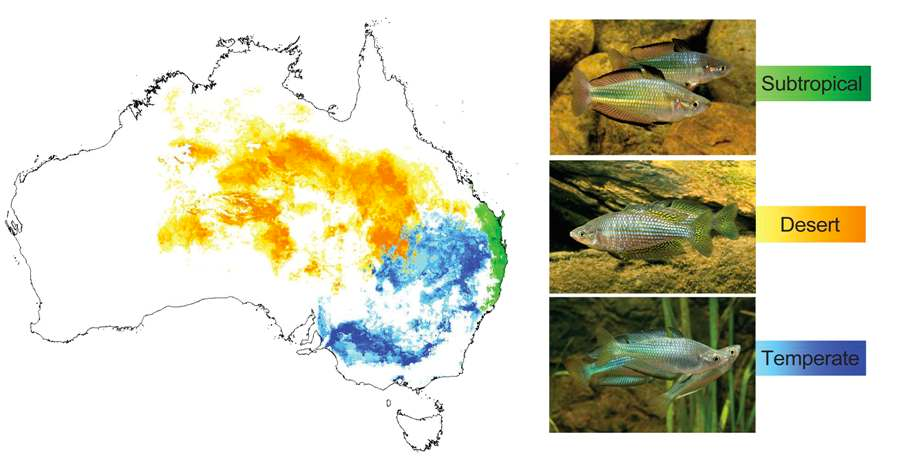 The range of the three study species of rainbowfishes in Australia. Photos by Gunther Schmida.
The range of the three study species of rainbowfishes in Australia. Photos by Gunther Schmida.
In the first study of its kind published in PNAS, Flinders University evolutionary biologists have shown that resilience or vulnerability to future climates is influenced by the thermal conditions of the climatic regions where species evolved.
The study compared thermal tolerance and gene expression (which genes are activated within a cell) in subtropical, desert and temperate Australian rainbowfishes.
Evolutionary biologist Professor Luciano Beheregaray says subtropical species were the winners in future climates because evolution suits their local conditions given these fish have the ability to turn on and off a larger number of heat stress genes in hotter climates.
The study shows that subtropical species have greater capacity to adapt to future climates than desert species, and that temperate species are the most vulnerable.
By looking at how all the genes are expressed in current temperatures and in temperatures projected for 2070, the researchers produced a catalogue of genes that informs about the adaptive capacity to climate change.
“Resilience or vulnerability to climate change is expected to be influenced by the thermal conditions where species are found, but we knew very little about this, and hardly anything about how this might vary across different climatic regions”, says co-author Dr Jonathan Sandoval-Castillo.
“Our results suggest that the vulnerability of species to climate change will be highly influenced by geographic factors, emphasising the value of assessments of climate traits for more accurate estimates of population impacts and the way ecosystems will ultimately respond”, says co-author and PhD student Katie Gates.
The findings can also be extended to many non-migratory species, aquatic or terrestrial, under pressure due to climate change.
“This information is important for identifying biodiversity at high risk of extinction and to develop ways to help them to adapt and persist. This includes restoring lost habitat and actively moving populations to more favourable climatic locations, while we still have time”, says Professor Beheregaray.
“Adaptation of plasticity to projected maximum temperatures and across climatically defined bioregions” by Flinders University evolutionary biologists Professor Luciano Beheregaray, Dr Jonathan Sandoval-Castillo, Katie Gates and Dr Chris Brauer and by collaborators Prof Louis Bernatchez (Université Laval, Canada) and Dr Steve Smith (University of Vienna, Austria) is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) 7 July 2020, https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/07/06/1921124117