Mountainous regions exhibit huge potential for hydropower that cannot be harnessed effectively by traditional technologies.
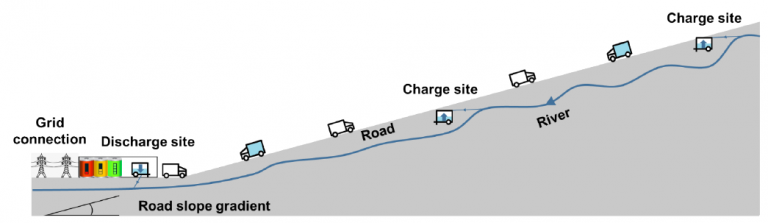 Figure: Schematic description of the system where the empty truck moves up the mountain to collect the containers filled with water at the charge site and the truck with the full container goes down the mountain generating electricity. The water is then unloaded at the discharge site. Image Credit: © Hunt et al., 2022.
Figure: Schematic description of the system where the empty truck moves up the mountain to collect the containers filled with water at the charge site and the truck with the full container goes down the mountain generating electricity. The water is then unloaded at the discharge site. Image Credit: © Hunt et al., 2022.
Julian Hunt, a researcher from the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA), and an international group of scientists have jointly come up with an innovative hydropower technology based on electric trucks. This innovative technology could offer a flexible and clean solution for the generation of electricity in mountainous regions.
In the shift towards a highly sustainable future, hydropower is likely to grow in significance as a renewable energy source. In spite of its potential, innovation in hydropower technology has been decelerating in the last century. Traditional techniques utilized at present depend on two connected reservoirs with various water levels where the potential energy of the water has been converted into electricity.
In steep mountain regions, the potential for producing electricity from a small stream of water is high. But the hydropower potential of such regions remains unused as it needs storage reservoirs, thereby posing social and environmental impacts.
A new technology known as Electric Truck Hydropower was developed by the IIASA researcher Julian Hunt and an international team of researchers. This could become a major technique for generating electricity in steep mountainous regions.
The study has been published in the journal Energy.
Electric Truck Hydropower would utilize the current road infrastructure to transport water down the mountain in containers, applying the regenerative brakes of the electric truck to convert the potential energy of the water into electricity and charge the truck’s battery.
Furthermore, the generated energy could be sold to the grid or utilized by the truck itself to transport other goods. Also, Electric Truck Hydropower could produce electricity jointly with solar and wind resources or offer energy storage services to the grid.
The ideal system configuration is in mountainous regions with steep roads, where the same electric trucks can be used to generate hydroelectric power from different locations. This increases the chances that water will be available.
Julian Hunt, Researcher, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
The suggested technology is an innovative, clean source of electricity that is competitive with wind, solar and conventional hydropower. Cost estimates illustrate that the levelized cost of Electric Truck Hydropower is US$30–100 per MWh, which is significantly cheaper compared to traditional hydropower at US$50–200 per MWh.
Also, the environmental impacts of Electric Truck Hydropower are considerably smaller compared to that of conventional hydropower.
This technology does not require dams, reservoirs, or tunnels, and it does not disrupt the natural flow of the river and fish passage. The system requires only roads, which already exist, charging and discharging stations similar to small car parks, a battery facility connected to the grid, and the trucks.
Julian Hunt, Researcher, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
Analyzing the global reach of this technology, the research group calculated that Electric Truck Hydropower could produce 1.2 PWh electricity annually, which is equivalent to around 4% of global energy consumption in 2019. The technology could tackle the earlier untapped potential for hydropower on steep mountain ranges. The regions with the greatest potential are the Andes and the Himalayas.
It is an interesting electricity generation alternative due to its high flexibility. For example, if a country is in an energy crisis, it can buy several electric trucks to generate hydropower. Once the crisis is over, the trucks can be used to transport cargo.
Julian Hunt, Researcher, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
Journal Reference:
Hunt, J. D., et al. (2022) Electric Truck Hydropower, a flexible solution to hydropower in mountainous regions. Energy. doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123495