Reviewed by Alex SmithMay 18 2022
Researchers identify the biological impacts and most beneficial hardness of extract-added water that has been derived from deep-sea water.
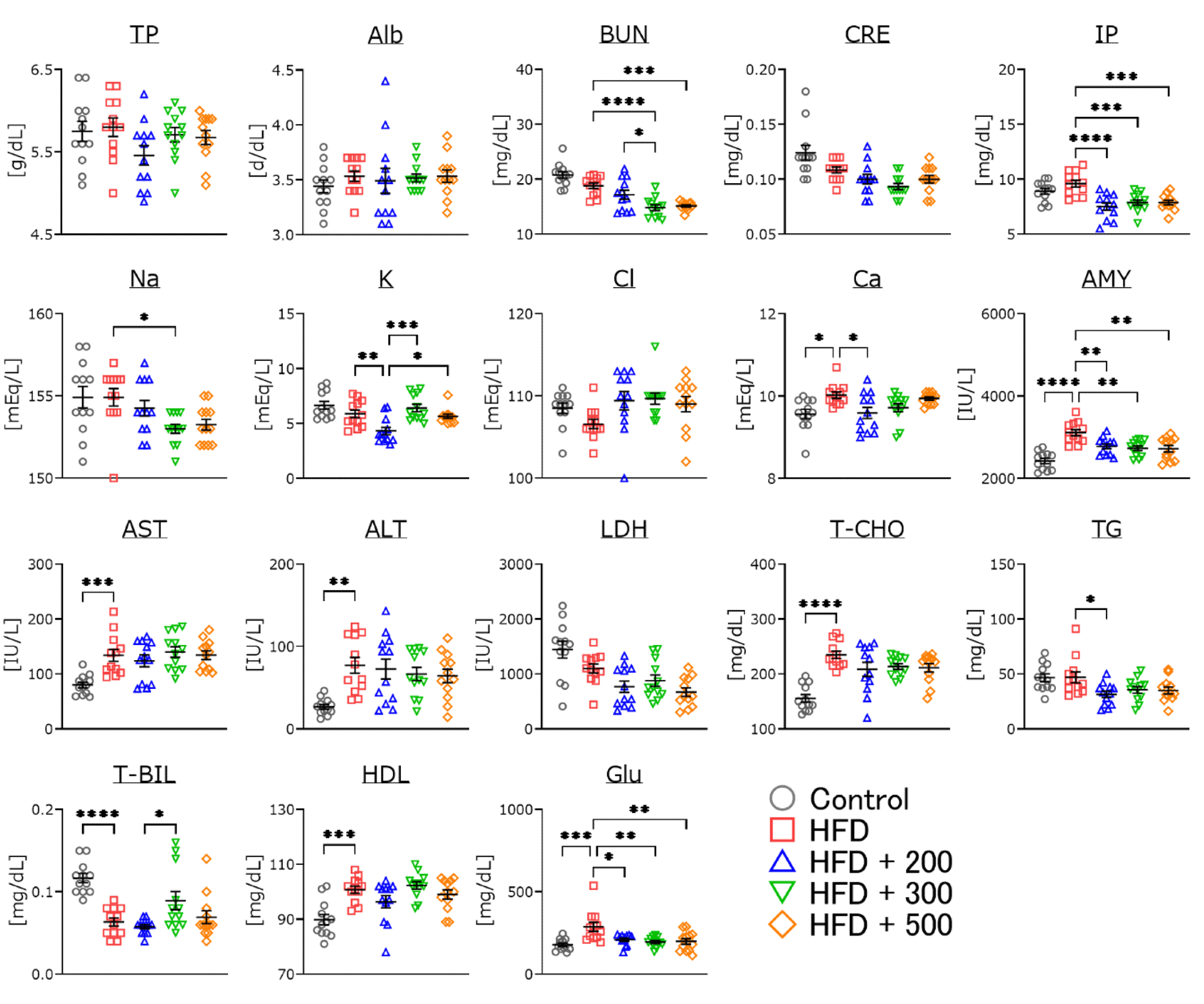 Shibaura Institute of Technology researchers investigate the effects of deep sea water extract-added water in obese mice. The figure shows a comparison of the changes in serum parameters for control, HFD-treated, and HFD-plus DSW-extract-added water-treated mice. Image Credit: Koji Fukui from SIT, Japan.
Shibaura Institute of Technology researchers investigate the effects of deep sea water extract-added water in obese mice. The figure shows a comparison of the changes in serum parameters for control, HFD-treated, and HFD-plus DSW-extract-added water-treated mice. Image Credit: Koji Fukui from SIT, Japan.
Deep-sea water (DSW) is considered a treasure trove of minerals like calcium, magnesium and potassium which are needed for significant functions. Drinking DSW-derived mineral water could have several health advantages.
Keeping this in mind, researchers from the Shibaura Institute of Technology have recently explored the biological impacts of DSW extract-added water in obese mice. Furthermore, they found out that the hardness of the water could have the greatest positive effect on health.
The oceans have helped maintain life on Earth for billions of years and will probably continue to do so. Oceans consist of an abundance of minerals like calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper and iron. These are considered to be essential nutrients for living organisms.
In Japan, deep-sea water (or DSW) is generally utilized for drinking, cosmetic purposes, and also as seasoning. Recent proof denotes that DSW has several health benefits. But the exact mechanism behind these advantages is yet to be known.
Furthermore, it is hard to compare mineral water sources like DSW as they have various hardnesses. Hardness denotes the number of minerals present in the water. Drinking water of a high hardness can be risky to humans.
A research group, headed by Professor Koji Fukui of Shibaura Institute of Technology (SIT) and including Yugo Kato, Ph.D., from SIT, Mr. Hirotsugu Takenaka from Dydo-Takenaka Beverage Co., Ltd., and Masahiro Kohno, Ph.D., from SIT, recently analyzed the biological impacts of DSW in obese mice.
Furthermore, they determined which hardness of DSW was most useful. The findings were reported in the journal nutrients on April 25th, 2022.
Initially, the scientists made DSW extract-added water of various levels of hardness (200, 300, and 500) from DSW taken off the coast of Muroto City, Kochi Prefecture. They then administered the DSW extract-added water to obese mice for a period of over two months and assessed if it had any impact on their coordinative and cognitive functions and also on their blood and biochemical parameters.
Such mice were compared with control mice that were fed the same high-fat diet but without DSW extract-added water. The impact of DSW on coordinative and cognitive functions was assessed via several tasks.
To identify the mechanism of cognitive improvement in the tests, the expression of neurotrophic factors and their receptors in the brain were assessed. Quantitative analysis was performed with the help of spectroscopy.
Although we did not observe an anti-obesity effect for any hardness level in the obese mice, the cognitive and coordinative functions of each DSW extract-added water-treated group were significantly improved compared to the control mice.
Koji Fukui, Professor, Shibaura Institute of Technology
Treatment which is done with DSW extract-added water considerably increased hippocampal NGF secretion in the obese mice.
Additionally, serum parameters like inorganic phosphorus, amylase, blood urea nitrogen, and glucose were reduced in the DSW extract-added water group than in the control group. This denotes a positive effect on renal function.
A qualitative analysis of DSW extract-added water at a hardness level of 300 disclosed greater concentrations of magnesium and potassium (11 and 7 times that of filtered tap water, respectively). Fascinatingly, sodium levels for water at this hardness level were reduced.
It is important to keep sodium ion concentrations low when concentrating DSW. It is well known that high sodium levels are a high-risk factor for diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular risk.
Koji Fukui, Professor, Shibaura Institute of Technology
The study outcomes of the scientists offer new insights on the number of mineral nutrients that are safe for chronic intake via drinking water. Professor Fukui commented on the extensive applications of this study.
A continued intake of beverages containing moderate mineral levels may help maintain proper health. It may reduce the risk of developing various age-related illnesses, such as renal disease, high blood pressure, cognition and coordination abilities, and lipid metabolism disorders.
Koji Fukui, Professor, Shibaura Institute of Technology
Journal Reference:
Fukui, K., et al. (2022) Effect of Extract-Added Water Derived from Deep-Sea Water with Different Hardness on Cognitive Function, Motor Ability and Serum Indexes of Obese Mice. nutrients. doi.org/10.3390/nu14091794.