The impact of meat production accounts for one of the largest proportions of greenhouse gas emissions in the food production industry. Therefore, developing new, futuristic methods to produce greener meat alternatives to animal farming is imperative to achieve current climate goals.
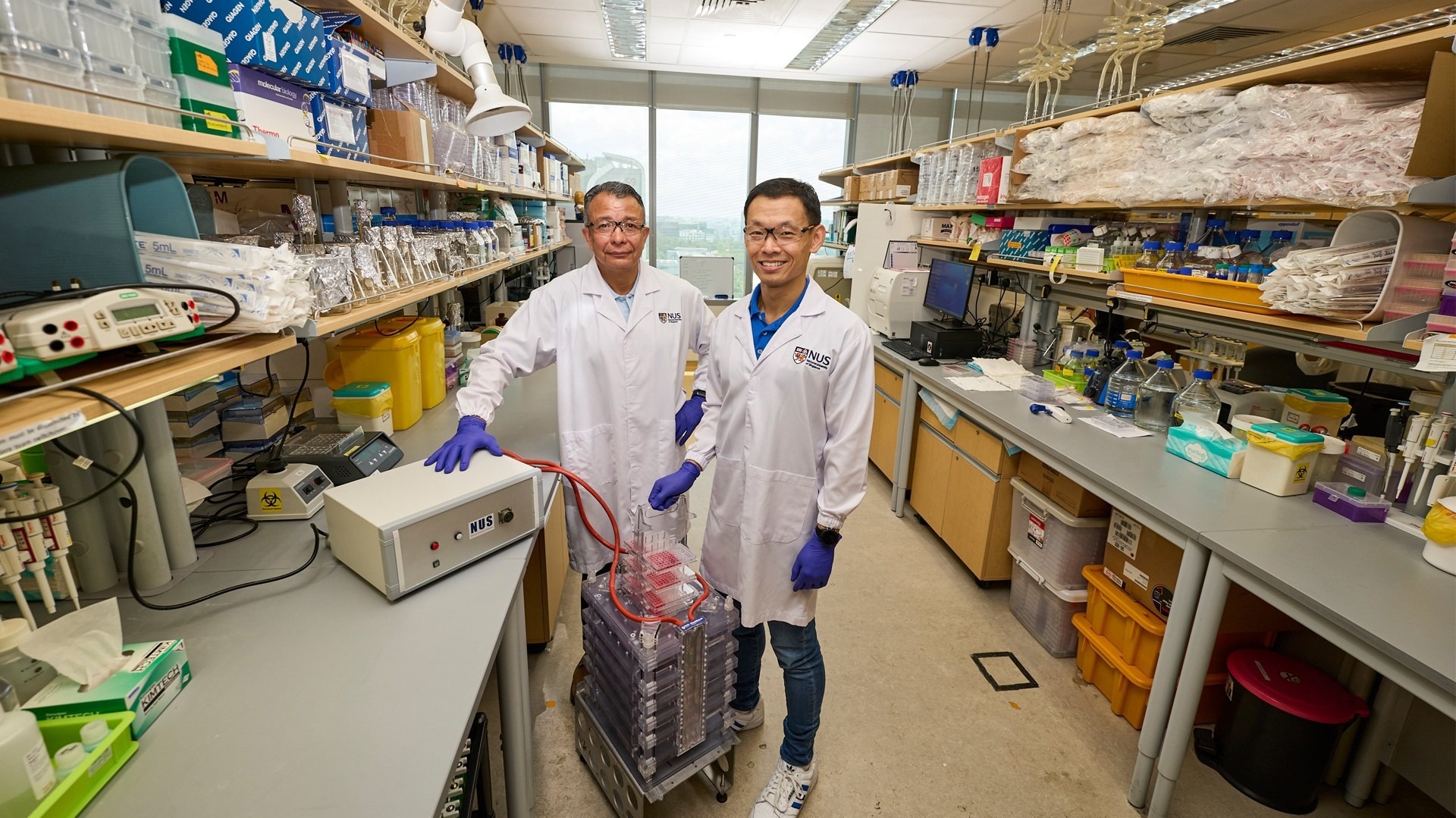

Image Credit: NUS
Finding eco-friendly alternatives to traditional farming methods is just one of the many methods that scientists hope will help combat the climate crisis.
One such area attracting a significant amount of attention is lab-grown meat, as it has the potential to be eco-friendly as it consumes less water and requires less water during cultivation. Another major advantage of lab-grown meat is that there are lower levels of emission of greenhouse gases.
Recently, a team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) developed an innovative technique that uses a magnetic field to grow meat in the lab in a more sustainable manner.
Details concerning the project have been published in the journal Biomaterials, in which the team presents their methodology, which, as well as having applications in the food production industry, could also offer countless other clinical and industrial benefits.
Magnetically Stimulated Cultured Meat
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured meat, does have great environmental potential, but it is also important to ensure that the energy and scaling-up methods do not outweigh other potential benefits of this typically complex and sophisticated process.
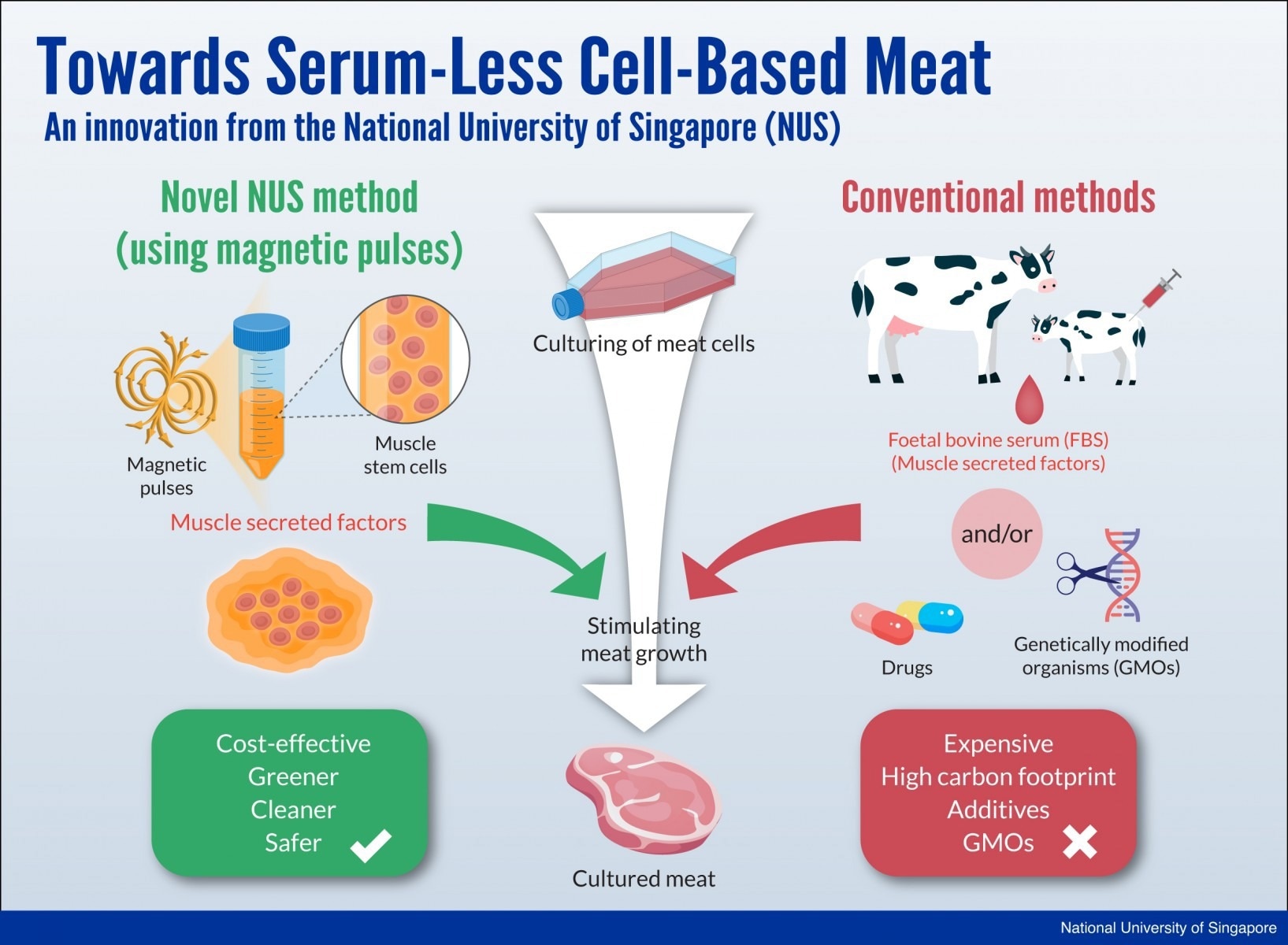
Image Credit: NUS
Furthermore, current cultured meat production methods still tend to use animal products or drugs to grow the meat in the lab, which could be considered counterintuitive. Typically, this involves feeding animal cells animal serum – fetal bovine serum (FBS) – to help them reproduce.
This method is still considered cruel as well as expensive in today’s lab-grown meat production process environment. Other methods generally use drugs or rely on genetic engineering to boost cell growth.
However, the technique developed by the team at NUS magnetically stimulates cells by applying a finely tuned pulsed magnetic field to cultivate myogenic stem cells found in animal skeletal muscle and bone marrow tissue. The meat growth is stimulated by the magnetic pulses, which produce a cultured meat product.
In response to a short 10-minute exposure to the magnetic fields, the cells release a myriad of molecules that have regenerative, metabolic, anti-inflammatory and immunity-boosting properties. These substances are part of what is known as the muscle “secretome” (for secreted factors) and are necessary for the growth, survival and development of cells into tissues.
Alfredo Franco-Obregón, Corresponding Author and Associate Professor, NUS
Cost-Effective, Greener, Cleaner, Safer
The team is excited by the possibility that one day in the future, their method and production of secretomes could replace FBS when harvesting lab-grown meat. This not only makes for a more cost-effective, less cruel way to culture the meat, but it would also be greener and safer.
This way, the myogenic stem cells will act as a sustainable and green bioreactor to produce the nutrients-rich secretomes for growing cell-based meat at scale for consumption. The muscle knows how to produce what it needs to grow and develop – it simply needs a little bit of encouragement when it is outside its owner. This is what our magnetic fields can provide.
Alfredo Franco-Obregón, Corresponding Author and Associate Professor, NUS
The next steps of the process include working with industry partners to attempt the commercialization and scaling up of this new novel method. If successful, eco-friendly lab-grown meat could be an excellent alternative to animal farming, potentially ushering in a new wave of sustainable food production practices.
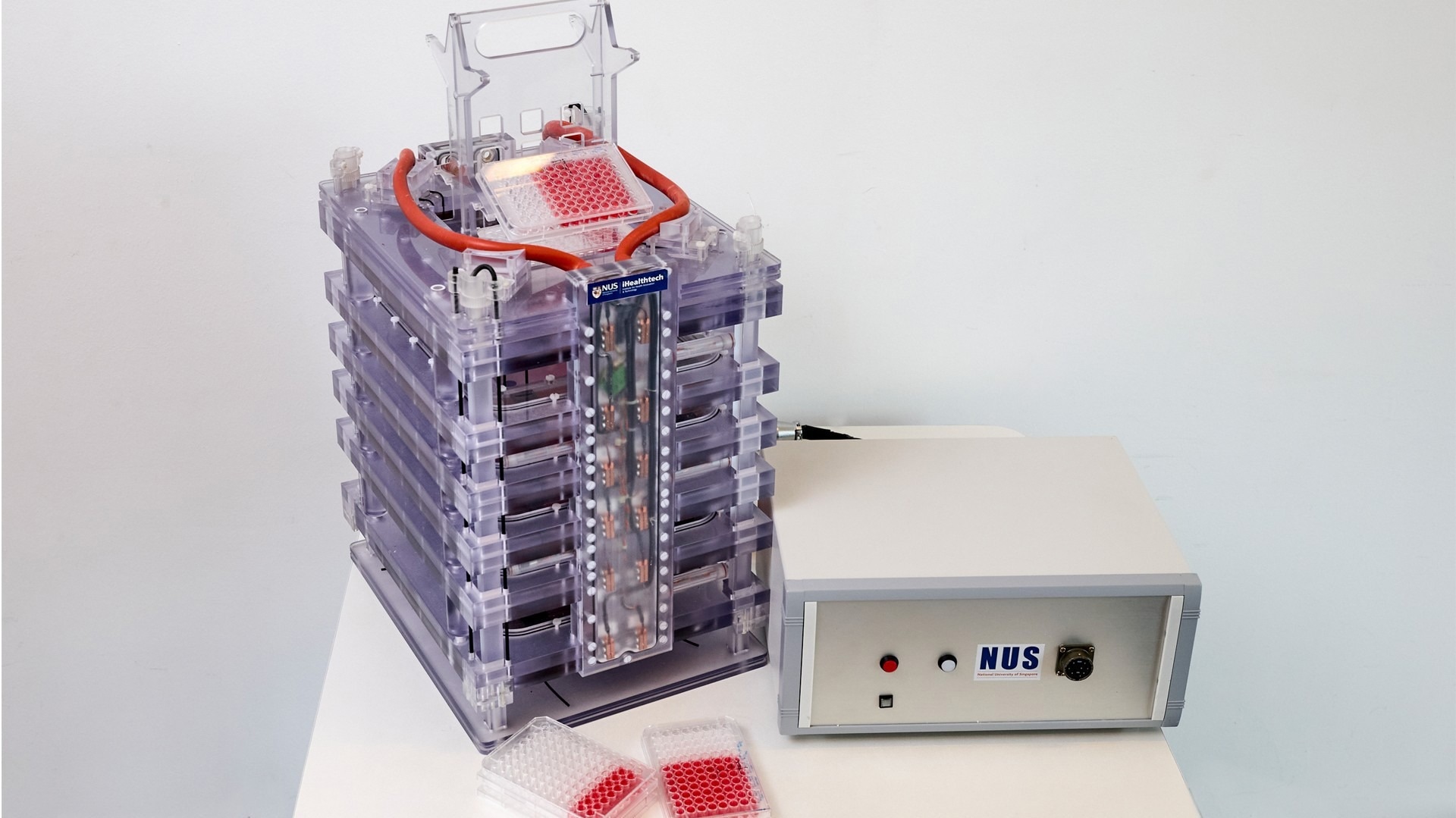

Image Credit: NUS
The team also tested their method on unhealthy cells and found that the technology could improve the recovery rate and regeneration of the cells. This opens up the potential to use magnetic pulse technology in regenerative medicine for use in a clinical setting.
By consuming less energy, water, and land, the meat of the future could help solve issues such as meeting supply chain demands while working towards climate goals.
References and Further Reading
Wong, C., Tai, Y., Yap, J., Fong, C. and Loo, L., et al., (2022) Brief exposure to directionally-specific pulsed electromagnetic fields stimulates extracellular vesicle release and is antagonized by streptomycin: A potential regenerative medicine and food industry paradigm. Biomaterials, [online] 287, p.121658. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961222002988?via%3Dihub
NUS scientists develop novel technique to grow meat in the lab using magnetic field. (2022) NUS scientists develop novel technique to grow meat in the lab using magnetic field. [online] Available at: https://news.nus.edu.sg/novel-technique-to-grow-meat-in-the-lab-using-magnetic-field/
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.